
Understanding the Ops Project: A Comprehensive Guide
Are you curious about the ins and outs of an Ops project? Whether you’re a seasoned professional or just dipping your toes into the world of operations, understanding the nuances of an Ops project can be crucial. In this detailed guide, we’ll delve into various aspects of an Ops project, providing you with a comprehensive understanding of what it entails.
What is an Ops Project?
An Ops project refers to a set of activities and tasks aimed at managing and optimizing the operations of an organization. These projects can range from improving IT infrastructure to enhancing customer support processes. The primary goal of an Ops project is to streamline operations, reduce costs, and improve efficiency.
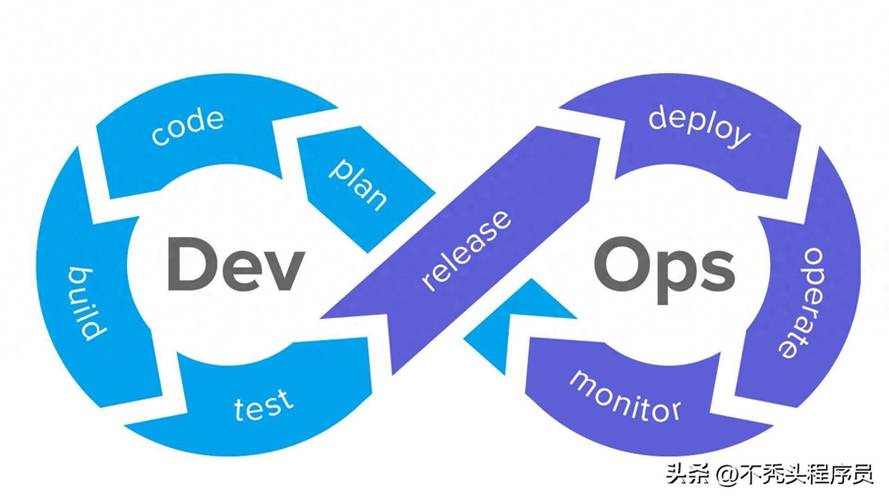
Key Components of an Ops Project
Understanding the key components of an Ops project is essential to grasp its full scope. Here are some of the critical elements:
-
IT Infrastructure Management: This involves overseeing the hardware, software, and network components that support an organization’s operations.
-
Process Optimization: Identifying and implementing improvements in existing processes to enhance efficiency and reduce waste.
-
Change Management: Ensuring that any changes made to the operations are smoothly implemented and do not disrupt the business.
-
Performance Monitoring: Tracking and analyzing the performance of various systems and processes to identify areas for improvement.
-
Resource Allocation: Efficiently distributing resources, such as personnel, budget, and time, to achieve project goals.
Stages of an Ops Project
Like any project, an Ops project goes through several stages. Here’s a brief overview:
-
Initiation: Identifying the project’s objectives, stakeholders, and scope.
-
Planning: Developing a detailed project plan, including timelines, resource allocation, and risk management strategies.
-
Execution: Implementing the project plan, coordinating resources, and managing any issues that arise.
-
Monitoring and Control: Tracking the project’s progress, ensuring that it stays on schedule and within budget, and making adjustments as needed.
-
Closure: Documenting the project’s outcomes, lessons learned, and celebrating successes.
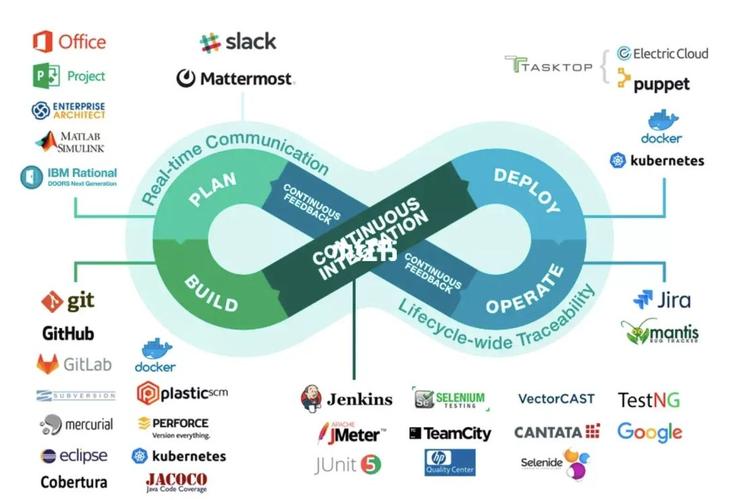
Tools and Technologies Used in Ops Projects
Ops projects often rely on a variety of tools and technologies to streamline operations and improve efficiency. Here are some commonly used tools:
| Tool | Description |
|---|---|
| JIRA | A project management tool that helps teams track issues and bugs, assign tasks, and manage sprints. |
| Ansible | An open-source automation tool that allows you to automate repetitive tasks, such as software deployment and configuration management. |
| Puppet | A configuration management tool that helps automate the deployment of software and systems across multiple environments. |
| Nagios | A monitoring tool that helps you track the performance and availability of your IT infrastructure. |
Challenges and Best Practices
While Ops projects offer numerous benefits, they also come with their own set of challenges. Here are some common challenges and best practices to overcome them:
-
Challenge: Resistance to change
Best Practice: Communicate the benefits of the project clearly and involve stakeholders in the decision-making process.
-
Challenge: Resource constraints
Best Practice: Prioritize tasks based on their impact and allocate resources efficiently.
-
Challenge: Lack of visibility
Best Practice: Implement monitoring tools and establish regular reporting to keep everyone informed.
Conclusion
Understanding the various aspects of an Ops project can help you navigate the complexities and achieve your organization’s goals. By focusing on key components, stages, tools, and best practices, you can ensure the success of your Ops project and drive continuous improvement in your organization’s operations.



