
Understanding the RIIo Op Amp: A Comprehensive Guide
When it comes to operational amplifiers (op-amps), the term RIIo can be quite intriguing. RIIo, which stands for “Rail-to-Input Offset,” is a crucial parameter that affects the performance of an op-amp. In this article, we will delve into the meaning of RIIo, its significance, and how it impacts the overall functionality of an op-amp. Let’s explore this fascinating topic together.
What is RIIo?
RIIo, or Rail-to-Input Offset, refers to the voltage difference between the positive and negative supply rails and the input terminals of an op-amp. It is an essential parameter that determines the accuracy and linearity of the op-amp’s output. In simpler terms, RIIo represents the voltage offset that occurs at the input terminals of the op-amp when the supply voltage is applied.
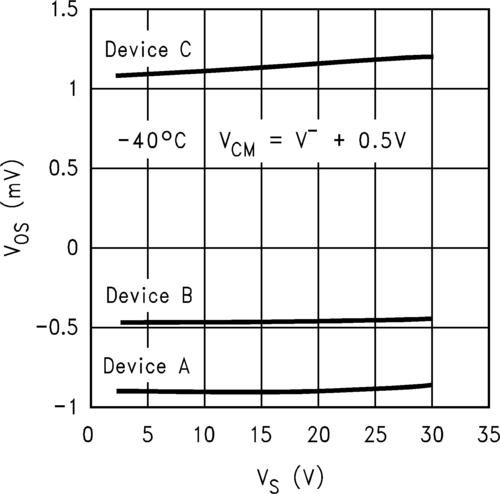
Understanding RIIo is crucial because it directly affects the accuracy of the op-amp’s output. A higher RIIo value indicates a larger voltage offset, which can lead to increased errors in the output signal. Conversely, a lower RIIo value ensures better accuracy and linearity in the op-amp’s performance.
Significance of RIIo
Now that we know what RIIo is, let’s explore its significance in the context of op-amps. Here are a few key points to consider:
-
Accuracy: RIIo plays a vital role in determining the accuracy of the op-amp’s output. A lower RIIo value ensures better accuracy, making the op-amp suitable for applications that require precise signal processing.
-
Linearity: RIIo affects the linearity of the op-amp’s output. A lower RIIo value results in better linearity, which is crucial for applications that demand high-fidelity signal reproduction.
-
Stability: RIIo contributes to the stability of the op-amp. A lower RIIo value ensures better stability, making the op-amp suitable for applications that require consistent performance over time.
-
Power Supply Rejection Ratio (PSRR): RIIo is closely related to the PSRR of an op-amp. A lower RIIo value results in better PSRR, which is essential for minimizing the impact of power supply fluctuations on the op-amp’s performance.
Impact of RIIo on Op-Amp Performance
The impact of RIIo on op-amp performance can be observed in various aspects. Let’s take a closer look at some of these aspects:
Input Offset Voltage
Input offset voltage is a direct consequence of RIIo. It represents the voltage difference between the two input terminals of the op-amp when the output is at zero. A higher RIIo value results in a larger input offset voltage, which can lead to increased errors in the output signal.
Drift
Drift refers to the change in the input offset voltage over time or temperature. A higher RIIo value can lead to increased drift, which can affect the stability and accuracy of the op-amp’s performance.
Non-Linearity
Non-linearity refers to the deviation of the op-amp’s output from an ideal straight line. A higher RIIo value can lead to increased non-linearity, which can affect the fidelity of the op-amp’s output signal.
Table: RIIo Values of Different Op-Amps
| Op-Amp Model | RIIo (mV) |
|---|---|
| LM741 | 2.5 |
| LM358 | 1.5 |
| OPA2134 | 0.5 |
| AD8605 | 0.1 |
As shown in the table above, the RIIo values of different op-amps vary significantly. The O




