
Understanding Post-Op Knee Crepitus: A Comprehensive Guide
Post-op knee crepitus is a term that might sound intimidating, but it’s a common experience for many individuals who have undergone knee surgery. Crepitus refers to the grating or crackling sound that you might hear or feel when you move your knee. This guide aims to provide you with a detailed understanding of post-op knee crepitus, its causes, symptoms, treatment options, and how to manage it effectively.
What is Post-Op Knee Crepitus?
Post-op knee crepitus occurs when there is abnormal movement or friction within the knee joint after surgery. This can happen due to various reasons, such as scar tissue formation, joint instability, or changes in the joint’s structure. It’s important to note that crepitus is not always a cause for concern, but it’s essential to understand its underlying causes and treatment options.
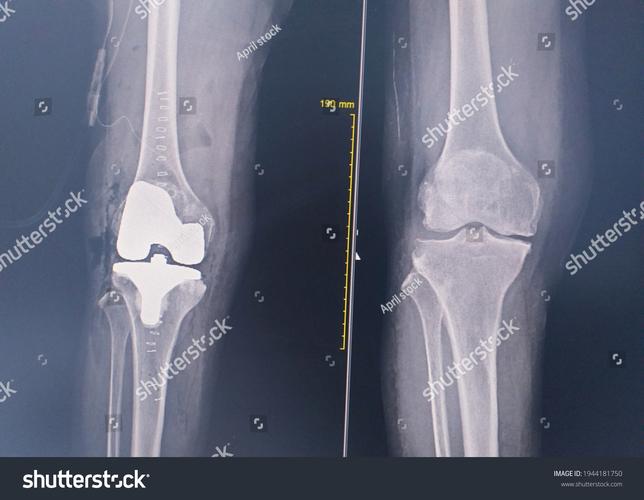
Causes of Post-Op Knee Crepitus
Several factors can contribute to the development of post-op knee crepitus:
| Factor | Description |
|---|---|
| Scar Tissue | Scar tissue can form around the knee joint, causing abnormal movement and friction. |
| Joint Instability | Instability in the knee joint can lead to abnormal movement and crepitus. |
| Changes in Joint Structure | Changes in the joint’s structure, such as osteoarthritis, can contribute to crepitus. |
| Improper Healing | Improper healing of the knee joint after surgery can lead to crepitus. |
Symptoms of Post-Op Knee Crepitus
The most common symptoms of post-op knee crepitus include:
- Grating or crackling sound when moving the knee
- Pain or discomfort in the knee joint
- Limited range of motion in the knee
- Sensitivity or tenderness in the knee area
Treatment Options for Post-Op Knee Crepitus
Treatment for post-op knee crepitus depends on the underlying cause and the severity of the condition. Here are some common treatment options:
- Physical Therapy: Physical therapy can help improve strength, flexibility, and stability in the knee joint.
- Medications: Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) can help reduce pain and inflammation.
- Bracing: A knee brace can provide support and stability to the joint.
- Injection Therapy: Injections, such as corticosteroids or hyaluronic acid, can help reduce pain and improve joint function.
- Surgery: In some cases, surgery may be necessary to correct the underlying cause of crepitus.
Managing Post-Op Knee Crepitus
Managing post-op knee crepitus involves a combination of lifestyle changes, home remedies, and medical treatment. Here are some tips to help you manage crepitus effectively:
- Stay Active: Regular exercise, such as walking, swimming, or cycling, can help improve joint function and reduce pain.
- Warm-Up and Cool-Down: Before and after exercise, it’s important to warm up and cool down to prevent injury and reduce pain.
- Use Heat or Ice: Applying heat or ice to the knee can help reduce pain and inflammation.
- Maintain a Healthy Weight: Excess weight can put additional stress on the knee joint, so maintaining a healthy weight is important.
- Seek Professional Advice: If you’re experiencing persistent pain or discomfort, it’s essential to consult with a healthcare professional for proper diagnosis and treatment.
In conclusion, post-op knee crepitus is a common experience for many individuals who have undergone knee surgery. Understanding its causes, symptoms, and treatment options can help you manage the condition effectively. Remember to stay proactive in your recovery and seek professional advice if you’re experiencing persistent pain or discomfort.




