
How to Calculate Gain of an Op Amp: A Detailed Guide
Understanding how to calculate the gain of an operational amplifier (op amp) is crucial for anyone working with analog circuits. The gain of an op amp determines how much it amplifies the input signal, and it’s a key factor in designing circuits that require precise signal processing. In this article, we’ll delve into the various methods and formulas used to calculate the gain of an op amp, providing you with a comprehensive understanding of this essential concept.
Understanding Op Amp Gain
Before we dive into the calculations, it’s important to understand what gain is in the context of an op amp. The gain of an op amp is defined as the ratio of the output voltage to the input voltage. It’s typically represented by the symbol ‘A’ and can be calculated using the following formula:
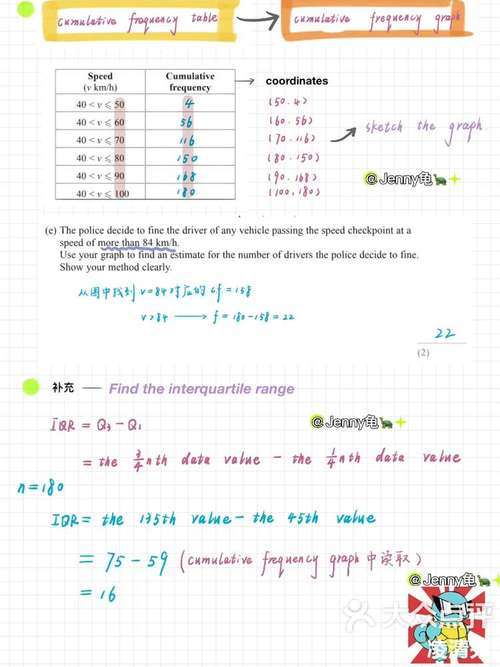
Gain (A) = Output Voltage (Vout) / Input Voltage (Vin)
It’s worth noting that the gain of an op amp is not fixed and can be adjusted using external components, such as resistors, capacitors, and inductors. This flexibility makes op amps highly versatile in various circuit applications.
Calculating Gain with a Simple Op Amp Configuration
One of the most common configurations for calculating the gain of an op amp is the non-inverting amplifier. In this configuration, the input signal is applied to the non-inverting input terminal (V+), and the output is taken from the output terminal. The gain of a non-inverting amplifier can be calculated using the following formula:
Gain (A) = 1 + (R2 / R1)
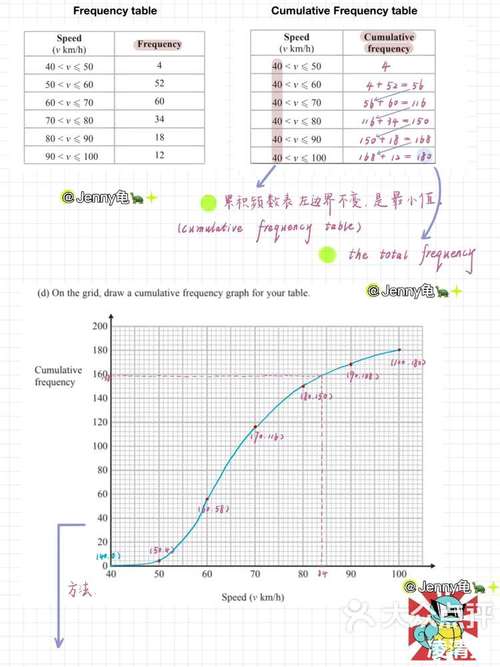
In this formula, R1 and R2 are the resistors connected to the inverting and non-inverting input terminals, respectively. The value of R2 is typically much larger than R1 to ensure a high gain.
Here’s an example to illustrate the calculation:
| Component | Value (Ohms) |
|---|---|
| R1 | 10 |
| R2 | 100 |
Using the formula, we can calculate the gain as follows:
Gain (A) = 1 + (100 / 10) = 11
Therefore, the non-inverting amplifier with these resistor values will have a gain of 11.
Calculating Gain with an Inverting Op Amp Configuration
The inverting amplifier configuration is another common way to calculate the gain of an op amp. In this configuration, the input signal is applied to the inverting input terminal (V–), and the output is taken from the output terminal. The gain of an inverting amplifier can be calculated using the following formula:
Gain (A) = – (R2 / R1)
In this formula, R1 and R2 are the resistors connected to the inverting and non-inverting input terminals, respectively. The value of R2 is typically much larger than R1 to ensure a high gain.
Here’s an example to illustrate the calculation:
| Component | Value (Ohms) |
|---|---|
| R1 | 10 |
| R2 | 100 |
Using the formula, we can calculate the gain as follows:
Gain (A) = – (100 / 10) = -10
Therefore, the inverting amplifier with these resistor values will




